As social media and online modes of communications are taking increasingly integral roles in our lives, the threat to privacy is increasing. Encryption becomes crucial for bank transactions, satellite communication, defense, and all modes of communication. Social media apps such as WhatsApp, Telegram and Facebook Messenger promise end-to-end encryption and a safe platform for conversations. However, scientists say that the methods of encryption are not as robust as they should be.
Keeping this in mind, an Indian scientist recently made a scientific breakthrough in making communication secure, in the domain of free-space quantum communications. Professor Urbasi Sinha, who heads the Quantum Information and Computing Lab, part of the Light and Matter Physics group at the Raman Research Institute (RRI) Bengaluru, has succeeded in securing quantum communication between two parties using an atmospheric free space channel.
“The conventional method in securing communication is to use encryption and decryption keys by processing algorithms in cryptography. However, the main issue is that the basis of encryption is the fundamental of mathematical complexity. The codes are written using complex mathematical problems, in a way that makes it difficult for the computers to decode,” Urbasi tells The Better India.
Breaking barriers
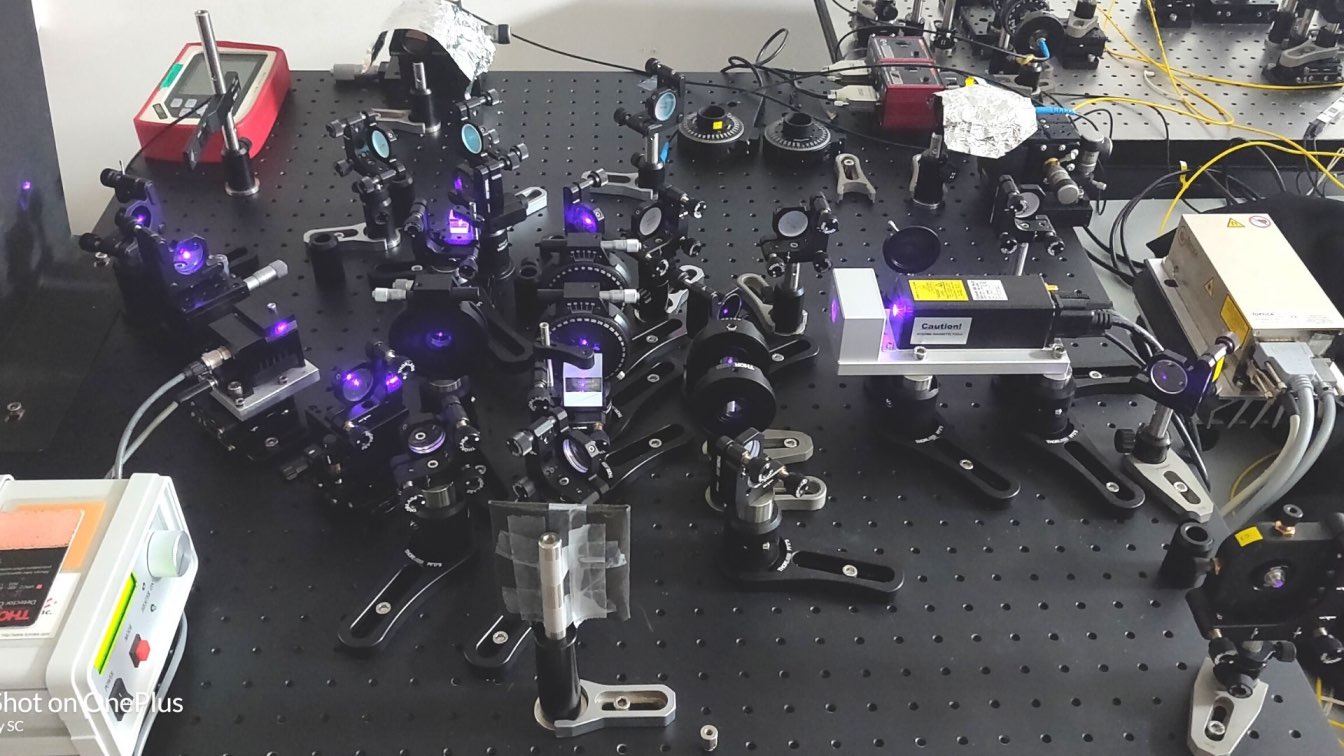
Urbasi explains that the conventional method becomes a problem, as it depends entirely on the computer’s ability and time required to decode encryptions. “The computers keep becoming advanced, and will soon be able to break encryption codes. For example, if a computer based on the previous configuration takes two hours to decode encryption, the advanced computer may do it in a matter of minutes. The security then becomes compromised,” she adds.
The scientist says the best way to solve the problem is to move to quantum technology. “The laws of nature are unbreakable and will ensure robust security. The technology involves using laws of nature, or more specifically, quantum physics to secure information,” she adds.
Urbasi says the quantum communications technology to exchange messages and information does exist, and is in practice. “But until now in India, it has only been confined within a room. People could send and receive messages in one room. But for longer distances, you either need either a fibre cable, or atmosphere. Using fibre cables will not prove to be a practical solution, as it requires enormous lengths of cable, and the losses would make it difficult to handle, as classical repeaters will not work in the quantum scenario. Such a practice would fail for long distances between countries and cities,” she adds.
No comments:
Post a Comment